APWeb 2016
The 18th Asia Pacific Web Conference
The Asia Pacific Web Conference, a leading international conference on research, development and applications of Web technologies, database systems, information management and software engineering, is aiming at attracting professionals of different communities such as industry and academic from not only Asia Pacific countries but also other continents. The objective is to share the experience in the area of the World Wide Web with the underlying technologies and applications.
Important Dates:
Camera-Ready Deadline: July 1, 2016
Author Registration Deadline: July 31, 2016
Conference Time: Sept 23 – Sept 25, 2016
About Suzhou
The long history of Suzhou City has left behind many attractive scenic spots and historical sites with beautiful and interesting legends. The elegant classical gardens, the old-fashioned houses and delicate bridges hanging over flowing waters in the drizzling rain, the beautiful lakes with undulating hills in lush green, and the exquisite arts and crafts, etc. have made Suzhou a renowned historical and cultural city full of eternal and poetic charm.
Suzhou is best known for its gardens: Humble Administrator's Garden, Lingering Garden, the Surging Wave Pavilion, and the Master of Nets Garden. These gardens weave together the best of traditional Chinese architecture, painting and arts.
Suzhou is also known as the "Venice of the East". The city is sandwiched between Taihu Lake and Grand Canal. Network of cannels, criss-crossed with hump-backed bridges, give Suzhou an image of City on the water.
Previous APWeb
Previous APWeb conferences were held in Beijing (1998), Hong Kong (1999), Xi'an (2000), Changsha (2001), Xi'an (2003), Hangzhou (2004), Shanghai (2005), Harbin (2006), Huangshan (2007), Shenyang (2008), Suzhou (2009), Busan (2010), Beijing (2011), Kunming (2012), Sydney (2013), Changsha(2014) and Guangzhou (2015).
APWeb 2016 will take place at Suzhou, China. It is a city with a long history on the lower reaches of the Yangtze River and on the shores of Lake Taihu in the province of Jiangsu, China.

Keynotes
Professor Zhi-Hua Zhou Nanjing University Title: Big Data Incremental Learning
Abstract: Traditional learning approaches usually try to collect all available data and then train a model. In big data applications, however, the data usually come in an accumulation or streaming way. Thus, it is more desirable to do incremental learning rather than training a new model from scratch when receiving new data. It is noteworthy that some important losses used in machine learning are quite challenging for incremental optimization. Moreover, in addition to new training samples, new classes may also occur. In this talk we will introduce some studies along this direction. Short Biography: Zhi-Hua Zhou is a Professor and Founding Director of the LAMDA Group at Nanjing University. He authored the book "Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms", and published more than 100 papers in top-tier journals and conference proceedings. His work have received more than 22,000 citations, with a h-index of 71. He also holds 14 patents and has good experiences in industrial applications. He has received various awards, including the National Natural Science Award of China, the IEEE CIS Outstanding Early Career Award, the Microsoft Professorship Award, 12 international journal/conference paper/competition awards, etc. He serves as the Executive Editor-in-Chief of Frontiers of Computer Science, Associate Editor-in-Chief of Science China, and Associate Editor of ACM TIST, IEEE TNNLS, etc. He founded ACML (Asian Conference on Machine Learning) and served as General Chair of ICDM’16, PAKDD’14, etc., Program Chair of IJCAI’15 Machine Learning track, SDM’13, etc. He also serves as Advisory Committee member for IJCAI 2015-2016, and Steering Committee Member of PAKDD and PRICAI. He is a Fellow of the AAAI, IEEE, IAPR, IET/IEE, CCF, and an ACM Distinguished Scientist. |
Professor Yufei Tao The University of Queensland Title: Small and Sweet MapReduce Algorithms Abstract: MapReduce has grown into a matured and powerful paradigm for large-scaled parallel computing. This keynote will introduce principles for designing algorithms on this paradigm that are both (i) small, i.e., they can be implemented in a real system with reasonable efforts, and (ii) sweet, i.e., they possess strong theoretical performance guarantees. Assuming little prior knowledge, we will start with the definition of the massively parallel computation (MPC) model, which has nowadays become a popular model in the database community for studying MapReduce algorithms. We will then move on to discuss MPC algorithms that can solve several fundamental database problems (particular, sorting and joins) optimally. The talk will end with several open problems exciting in the eyes of the speaker. Short Biography: Yufei Tao is a Professor at the School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, the University of Queensland (UQ). Prior to joining UQ, he held professorial positions at the City University of Hong Kong, the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). He served as an associate editor of ACM Transactions on Database Systems (TODS) from 2008 to 2015, and of IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (TKDE) from 2012 to 2014. He was a PC chair of International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) 2014, and of International Symposium on Spatial and Temporal Databases (SSTD) 2011. He was a keynote speaker at International Conference on Database Theory (ICDT) 2016, and a winner of the SIGMOD best paper award in 2013 and 2015. |
Professor Cyrus Shahabi University of Southern California (USC) Title: Inference of Social Relationships from Location Data Abstract: For decades, social scientists have been studying people's social behaviors by utilizing sparse datasets obtained by observations and surveys. These studies received a major boost in the past decade due to the availability of web data (e.g., social networks, blogs and review web sites). However, due to the nature of the utilized dataset, these studies were confined to behaviors that were observed mostly in the virtual world. Differing from all the earlier work, here, we aim to study social behaviors by observing people's behaviors in the real world. This is now possible due to the availability of large high-resolution spatio-temporal location data collected by GPS-enabled mobile devices through mobile apps (Google's Map/Navigation/Search/Chrome, Facebook, Foursquare, WhatsApp, Twitter) or through online services, such as geo-tagged contents (tweets from Twitter, pictures from Instagram, Flickr or Google+ Photo), etc. In particular, we focus on inferring two specific social measures: 1) pair-wise strength -- the strength of social connections between a pair of users, and 2) pair-wise influence - the amount of influence that an individual exerts on another, by utilizing the available high-fidelity location data representing people's movements. Finally, we argue that due to the sensitivity of location data and user privacy concerns, these inferences cannot be largely carried out on individually contributed data without privacy guarantees. Hence, we discuss open problems in protecting individuals'location information while enabling these inference analyses.
|
Distinguished Lecture Series
Professor Chen Li University of California, Irvine Title: Real-Time Analytics and Visualization on Large-Scale Spatial-Temporal-Textual Data Abstract: We are developing a system called Cloudberry to support analytics and visualization on large data sets with spatial, temporal, and textual attributes, such as social media data and query logs. It supports aggregation queries on various types of attributes, and allows efficient data exploration at different granularities (e.g., state, county, and city). It also supports real-time analytics, which can allow applications to monitor “what’s happening now.” To achieve a high speed, it includes an intelligent middleware for view materialization and cache management. As a general-purpose solution for large data sets, it uses the Apache AsterixDB big data management system that provides rich features and high performance, such as various indexes and data feeds. In this talk, we will give an overview of the system, our initial results, and open challenges in this direction. A live demonstration using tweets is available at http://cloudberry.ics.uci.edu/ . Short Biography: Chen Li is a professor in the Department of Computer Science at UC Irvine. He received his Ph.D. degree in Computer Science from Stanford University, and his M.S. and B.S. in Computer Science from Tsinghua University, China, respectively. His research interests are in the field of data management, including data cleaning, data integration, data-intensive computing, and text analytics. He was a recipient of an NSF CAREER Award, several test-of-time publication awards, and many other grants and industry gifts. He was once a part-time Visiting Research Scientist at Google. He founded a company SRCH2 to develop an open source search engine with high performance and advanced features. |
Professor Jianliang Xu Hong Kong Baptist University Title: Towards Interactive and Social-Aware Spatial Query Services Abstract: Location-based service (LBS) have been gaining in prominence, with about 40% of world's population using smartphones today. As such, there is a growing need to continuously advance the spatial database research for emerging LBS applications, which pose new challenges as well as new opportunities. For example, the convergence of location data and social media has enabled a new class of geo-social queries that combine location and social factors in query processing. In addition, to enhance system usability and user experience, it is important to support instantaneous and interactive responses to queries. In this talk, we will present several of our recent efforts on geo-social queries and "why-not"/"what-if" interactive queries that are aimed to improve the functionality, usability, and performance of spatial query services. We will also discuss some possible future research directions. |
Tutorials
Professor Kun-Ta Chuang National Cheng Kung University Title : Data Science for Epidemic Computing Abstract: The control of epidemic spread is the critical challenge for the authority in recent decades. When people are moving to live in the urban area, the crowded situation inevitably increases the outbreak probability of some contagious diseases such as flu and dengue fever. For the need to prevent the out-of-control infections, it is necessary to develop new technologies, predicting and evaluating the prevention result along with the dynamic deployment of intervention strategies over time. In this tutorial, we will introduce some mechanisms from data science and discuss their extension applied in the outbreak control during the spread of dengue fever in Taiwan 2015. We will also discuss the intervention procedure in Taiwan and show the way to incorporate data mining idea for epidemic computing into the process of decision making in the government side. The audience will know the basic concept of public health and learn the way to devise new computational algorithms for this critical challenge.
|
Professor Hyeonsang Eom Seoul National University Title: Workload-Aware Resource Management Technologies for Improving Server Performance Abstract: Datacenters where various sorts of servers may run have been becoming larger and more heterogeneous, possibly being highly distributed. It is crucial to manage many heterogeneous resources effectively to efficiently and cost-effectivity provide services; it is necessary to allocate “right” resources to Virtual Machines (VMs) in virtualized datacenters in order to decrease the cost of the operation while meeting the SLAs (Service Level Agreements) such as meeting the latency requirement. One of the most effective ways to allocate “right” resources to a VM would be to do it considering the characteristics of the VM such as the memory intensiveness of the workload executed in the VM. However, the existing schedulers do not consider these kinds of characteristics, including the NOVA scheduler of OpenStack and DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) of VMWare. In this tutorial, I explain some workload-aware schedulers, and our workload-aware one that schedules VMs on OpenStack clusters of nodes, considering the characteristics of workload executed in the VMs. Our experimental study with Redis and Memcached possibly caching the data and links of Web servers shows that our memory-intensiveness-aware scheduler may outperform the default scheduler of OpenStack and DRS as well in terms of throughput and latency. Short Biography: Hyeonsang Eom received the BS degree in computer science and statistics from Seoul National University (SNU), Seoul, Korea, in 1992, and the MS and PhD degrees in computer science from the University of Maryland at College Park, Maryland, USA, in 1996 and 2003, respectively. He is currently an associate professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at SNU, where he has been a faculty member since 2005. He was an intern in the data engineering group at Sun Microsystems, California, USA, in 1997, and a senior engineer in the Telecommunication R&D Center at Samsung Electronics, Korea, from 2003 to 2004. His research interests include distributed systems, cloud computing, operating systems, high performance storage systems, energy efficient systems, fault-tolerant systems, security, and information dynamics. |

Workshops
2nd International Workshop on Web Data Mining and Applications (WDMA 2016)
http://ada.suda.edu.cn/apweb2016/WDMA_2016.html
1st International Workshop on Graph Analytics and Query Processing (GAP 2016)
http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~gap
1st International Workshop on Spatio-temporal Data Management and Analytics (SDMA’2016)
http://ada.suda.edu.cn/apweb2016/SDMA2016/
Accepted Papers
Research Full Paper
Probabilistic Nearest Neighbor Query in Traffic-Aware Spatial Networks
NERank: Bringing Order to Named Entities from Texts
FTS: A Practical Model for Feature-based Trajectory Synthesis
Distributed Text Representation with Weighting Scheme Guidance for Sentiment Analysis
A Real Time Wireless Interactive Multimedia System
Forecasting Career Choice for College Students Based on Campus Big Data
Efficient Group Top-k Spatial Keyword Query Processing
Online Prediction for Forex with an Optimized Experts Selection Model
Flexible and Adaptive Stream Join Algorithm
Practical Study of Subclasses of Regular Expressions in DTD and XML Schema
Finding Frequent Items in Time Decayed Data Streams
Fast Rare Category Detection Using Nearest Centroid Neighborhood
Scalable Private Blocking Technique for Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage
Learn to recommend local event using heterogeneous social networks
Latent Semantic Diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Top-k Temporal Keyword Query over Social Media Data
Correlation-based Weighted k-Labelsets for Multi-Label Classification
Classifying Relation via Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network based on Local Information
Psychological Stress Detection from Online Shopping
When a Friend Online is More Than a Friend in Life: Intimate Relationship Prediction in Microblogs
Community Inference with Bayesian Symmetric Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
Confidence-learning based collaborative filtering with heterogeneous implicit feedbacks
Spica: A Path Bundling Model for Rational Route Recommendation
Mining Co-locations from Continuously Distributed Uncertain Spatial Data
An Online Approach for Direction-Based Trajectory Compression with Error Bound Guarantee
A Target-dependent Sentiment Analysis Method for Micro-blog Streams
Maximizing the influence ranking under limited Cost in social network
A Data Grouping CNN Algorithm for Short-term Traffic Flow Forecasting
Repair Singleton IDs on the Fly
Making Cold Data Identification Efficient in Non-Volatile Memory Systems
Star-Scan : A Stable Clustering by Statistically Finding Centers and Noises
Aggregating Crowd Wisdom with Instance Grouping Methods
FHSM: Factored Hybrid Similarity Methods for Top-N Recommender Systems
Accelerating Path Nearest Neighbor Search in Spatial Networks
Man-O-Meter: Modeling and Assessing the Evolution of Language Usage of Individuals on Microblogs
Modeling for Noisy Labels of Crowd Workers
Online Streaming Feature Selection using Sampling Techniques and Correlations between Features
CoDS:Co-training with Domain Similarity for Cross-domain Image Sentiment Classification
Personalized Resource Recommendation Based on Regular Tag and User Operation
Academic Paper Recommendation Based on Community Detection in Citation-Collaboration Networks
Budget Minimization with Time and Influence Constraints in Social Network
Feature Selection via Vectorizing Feature's Discriminative Information
Incomplete Data Classfication Based on Multiple Views
Preference Join on Heterogeneous Data
A Label Inference Method based on Maximal Entropy Random Walk over Graphs
An Adaptive kNN Using Listwise Approach for Implicit Feedback
Accelerating Time Series Shapelets Discovery with Key Points
Quantifying the Effect of Sentiment on Topic Evolution in Chinese Microblog
Efficient Evaluation of Shortest Travel-time Path Queries in Road Networks by Optimizing Waypoints in Route Requests through Spatial Mashups
Improving Recommendation Accuracy for Travelers by Exploiting POI Correlations
Fuzzy Keywords Query
Towards Efficient Influence Maximization for Evolving Social Networks
Detecting Community Pacemakers of Burst Topic in Twitter
Dynamic User Attribute Discovery on Social Media
Improving Temporal Recommendation Accuracy and Diversity via Long and Short-Term Preference Transfer and Fusion Models
Measuring Directional Semantic Similarity with Multi-Features
Discovering Companion Vehicles from Live Streaming Traffic Data
EPLA:Efficient Personal Location Anonymity
The Competition of User Attentions Among Social Network Services: a Social Evolutionary Game Approach
An Adaptive Partition-Based Caching Approach for Efficient Range Queries on Key-value Data
Mechanism Analysis of Competitive Information Synchronous Dissemination in Social Networks
A Context-aware Method for Top-k Recommendation in Smart TV
A Topic-Specific Contextual Expert Finding Method in Social Network
Real-time Anomaly Detection over ECG Data Stream Based on Component Spectrum
Near-Duplicate Web Video Retrieval and Localization Using Improved Edit Distance
Finding Latest Influential Research Papers through Modeling Two Views of Citation Links
Handling Estimation Inaccuracy in Query Optimization
An Approach for Cross-Community Content Recommendation: A Case Study on Docker
Multi-label Chinese Microblog Emotion Classification via Convolutional Neural Network
Mining Recent High Expected Weighted Itemset from Uncertain Databases
Context-aware Chinese Microblog Sentiment Classification with Bidirectional LSTM
A Secure and Robust Covert Channel Based on Secret Sharing Scheme
A Hybrid Method for POI Recommendation: Combining Check-in Count, Geographical Information and Reviews
A Workload-Driven Vertical Partitioning Approach Based on Streaming Framework
Time-Constrained Sequenced Route Query in Indoor Spaces
Discovering Approximate Functional Dependencies from distributed big data
B-mine: Frequent Pattern Mining and Its Application to Knowledge Discovery from Social Networks
An Efficient Online Event Detection Method for Microblogs via User Modeling
Research Short Paper
Microblog Sentiment Analysis Based on Sentiment Features
FVBM: A Filter-Verification-Based Method for Finding Top-k Closeness Centrality on Dynamic Social Networks
Online Hot Topic Detection from Web News Based on Bursty Term Identification
Grouped Team Formation in Social Networks
Profit Maximizing Route Recommendation for Vehicle Sharing Requests
Ontology-Based Interactive Post-Mining of Interesting Co-location Patterns
AALRSMF: An Adaptive Learning Rate Schedule for Matrix Factorization
A Graph Clustering Algorithm for Citation Networks
A Distributed Frequent Itemsets Mining Algorithm Using Sparse Boolean Matrix on Spark
A Simple Stochastic Gradient Variational Bayes for the Correlated Topic Model
Reasoning with Large Scale OWL 2 EL Ontologies based on MapReduce
Purchase and Redemption Prediction based on Multi-task Gaussian Process and Dimensionality Reduction
RORS: Enhanced Rule-based OWL Reasoning on Spark
A Hadoop-based Database Querying Approach for Non-expert Users
A Collaborative Join Scheme on a MIC-based Heterogeneous Platform
Pairwise Expansion: A New Topdown Search for mCK Queries Problem over Spatial Web
Mentioning the optimal users in the appropriate time on Twitter
Historical Geo-Social Query Processing
WS-Rank: Bringing Sentences into Graph for Keyword Extraction
Efficient Community Maintenance for Dynamic Social Networks
Open Sesame! Web Authentication Cracking via Mobile App Analysis
K-th Order Skyline Queries in Bicriteria Networks
A K-Motifs Discovery Approach for Large Time-Series Data Analysis
User Occupation Prediction on Microblogs
Similarity Recoverable, Format-preserving String Encryption
Industry Full Paper
Combo-Recommendation based on Potential Relevance of Items
Demo Paper
OPGs-Rec: Organized-POI-Groups Based Recommendation
A Demonstration of Encrypted Logistics Information System
PCMiner:An Extensible Framework for Analysing and Detecting Protein Complexes
MASM:A Novel Movie Analysis System based on Microblog
A Text Retrieval System Based on Distributed Representations
A System for Searching Renting Houses Based on Relaxed Query Answering
TagTour: a Personalized Tourist Resource Recommendation System
A Chronic Disease Analysis System Based on Dirty Data Mining
ADDS: An Automated Disease Diagnosis-aided System
INDOOR MAP SERVICE SYSTEM BASED ON WECHAT TWO-DIMENSIONAL CODE
Factorization machine based business credit scoring by leveraging Internet data
OICRM:An Ontology-based Interesting Co-location Rule Miner
CB-CAS: a CAS-Based Cross-Browser SSO System
A Demonstration of QA System based on Knowledge Base
An Alarming and Prediction System for Infections Disease Baced on Combined Modles
Co-location Detector: A System to Find Interesting Spatial Co-locating Relationships
KEIPD:Knowledge Extraction and Inference System for Personal Documents
Workshop Papers
International Workshop on Web Data Mining and Applications (WDMA 2016)
Maximizing the Cooperative Influence Spread in a Social Network Oriented to Viral Marketing
A Multi-Model Based Approach for Big Data Analytics: the Case on Education Grant Distribution
Sentiment Target Extraction Based on CRFs with Multi-features for Chinese Microblog
EMD-DSJoin: Efficient Similarity Join over Probabilistic Data Streams Based on Earth Mover’s Distance
Sentiment Analysis on User Reviews through Lexicon and Rule-based Approach
Social Link Prediction Based on the Nodes' Information Transfer
An Improved ML-kNN Approach Based on Coupled Similarity
A Novel Recommendation Method Based on User’s Interest and Heterogeneous Information
Knee point-driven bottleneck detection algorithm for cloud service system
Confirmatory Analysis on Influencing Factors When Mention Users in Twitter
A stock recommendation strategy based on M-LDA model
Short-term Forecasting and Application about Indoor Cooling Load Based on EDA-PSO-BP Algorithm
International Workshop on Graph Analytics and Query Processing (GAP 2016)
Identifying Relevant Subgraphs in Large networks
User-dependent Multi-relational Community Detection in Social Networks
Compressing Streaming Graph Data Based on Triangulation
International Workshop on Spatio-temporal Data Management and Analytics (SDMA’2016)
Scene Classification in High Resolution Remotely Sensed Images based on PCANet
Finding Top-k Places for Group Social Activities
Temporal Spatial-Keyword Search On Databases Using SQL
Features of Rumor Spreading on WeChat Moments
Distance-Based Continuous Skylines On Geo-Textual Data
Improving Urban Traffic Evacuation Capability in Emergency Response by Using Smart Phones
Context Enhanced Keyword Extraction for Sparse Geo-entity Relation from Web Texts
A Stacked Generalization Framework for City Traffic Related Geospatial Data Analysis
Detection of Statistically Signi cant Bus Delay Aggregation by Spatial-Temporal Scanning
Acquisition and Representation of Knowledge for Academic Field
Using Learning Features to Find Similar Trajectories
An Algorithm for Mining Moving Flock Patterns from Pedestrian Trajectories

Conference Program
Program at a Glance

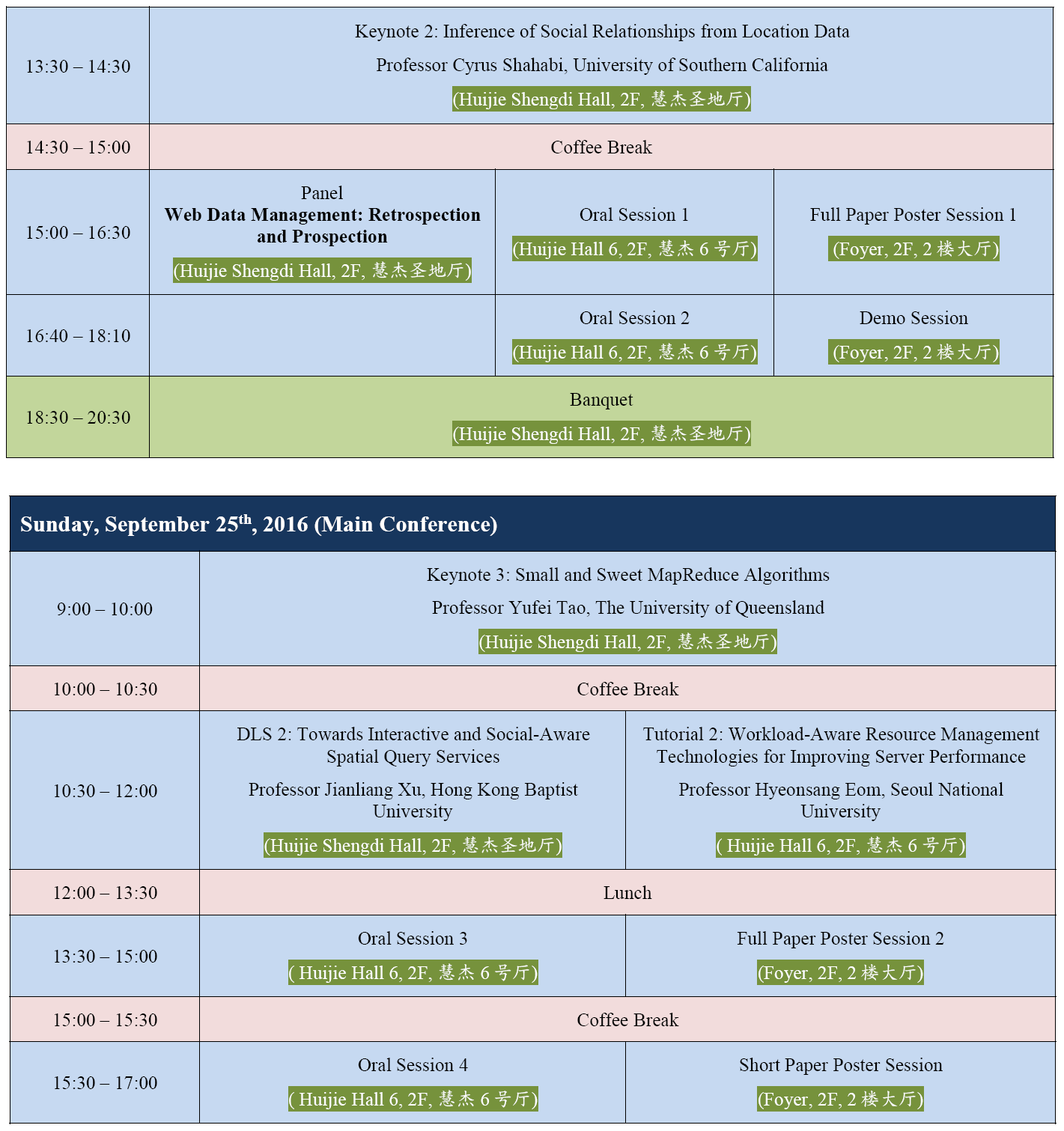
Detailed Program can be found in ![]() Program-v17.pdf. Should you find anything unclear or incorrect, please let us know.
Program-v17.pdf. Should you find anything unclear or incorrect, please let us know.
Conference Venue
Suzhou Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool International Conference Center(苏州西交利物浦国际会议中心)
Location: No. 99 Renai Road, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Provice, P.R.China
Tel: +86-512-86665555 Introduction: http://05286665555.locoso.com
The conference venue is 20 minutes drive from Suzhou Railway Station (苏州火车站) and 30 minutes drive from Suzhou Highspeed Train Station (苏州高铁北站). Taxi is the most convenient way to get there.
|










